The risks of switching your industrial parts cleaner
Realizing the benefits of
taking TCO into consideration
for industrial cleaning
Table of Contents
The risks of switching your industrial parts cleaner
Changing your industrial cleaning chemical is not an insignificant decision. If you are a production manager or process engineer, you already know this. There is downtime to plan for, a new product to validate, and a team to bring along. The risks are real.
This post does not pretend otherwise. We will walk through the most common concerns about switching industrial parts cleaners, one by one, and take them seriously. Because they deserve to be taken seriously.
Then, at the end, we will ask a different question.
Risk 1. Production downtime
Any conversion to a new cleaning chemical requires the wash bath to be drained, the machine to be cleaned, and the new product to be dosed and brought up to temperature. That takes time. Depending on your machine size, contamination levels and wastewater handling setup, it could mean several hours of non-production.
For a busy production line, that is a legitimate concern. Unplanned downtime costs money, and the pressure to keep things moving is constant.
This risk is real. It is also manageable. A conversion that is properly planned, scheduled during a maintenance window and handled by an experienced technician is a different proposition from one that is improvised on a Tuesday afternoon. The risk is not in the switching. It is in switching without a plan.
Risk 2. Cleaning quality during the conversion
A new cleaning product behaves differently. Bath chemistry takes time to stabilise. There is a period of adjustment, and during that period, your cleaning results may not be exactly what you are used to.
This is a fair concern, particularly in industries where cleanliness specifications are tight, such as automotive, hydraulics or precision engineering. A rejected part is not an abstract problem. It costs time, material and credibility.
The way to manage this risk is through proper pre-testing. A cleaning product that has been validated against your specific parts, contaminants and machine setup before the conversion is not a gamble. It is a confirmed outcome. The risk exists when you skip that step.
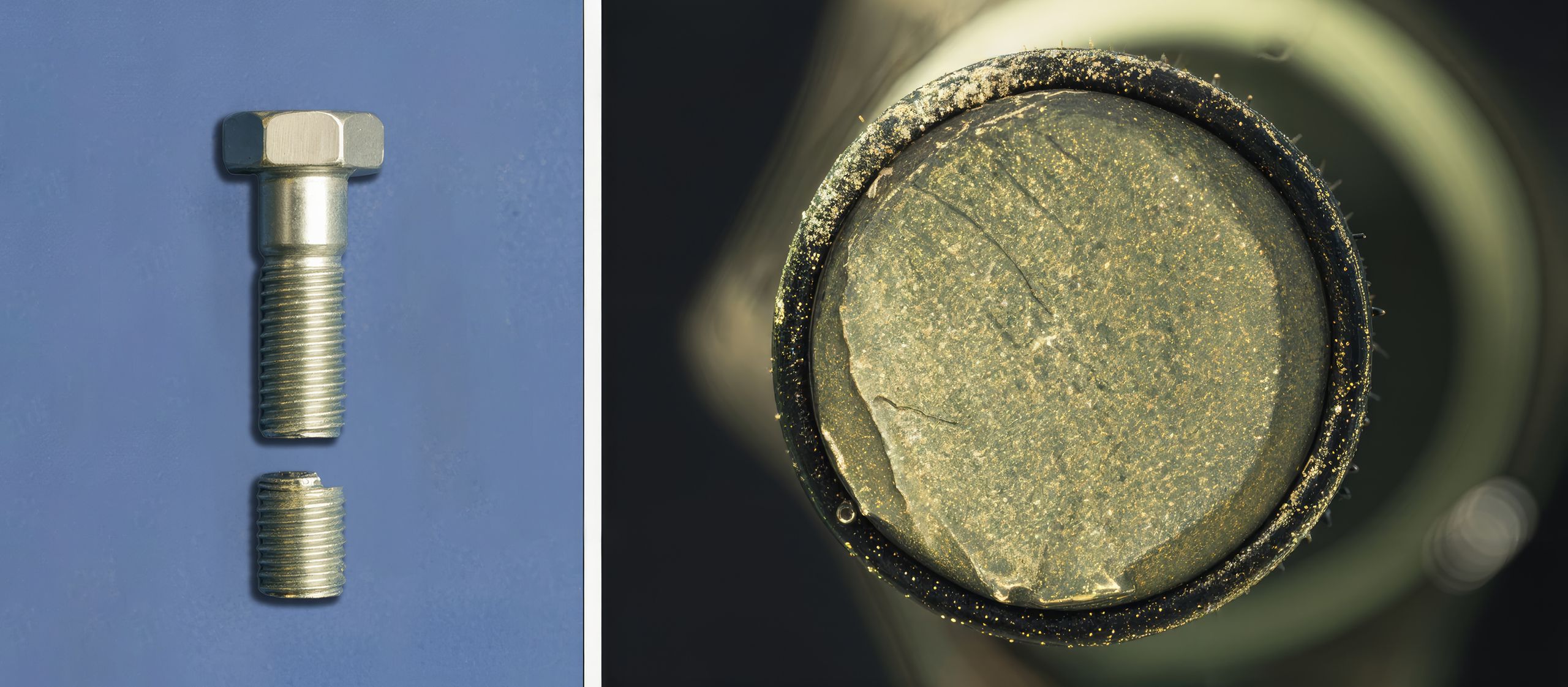
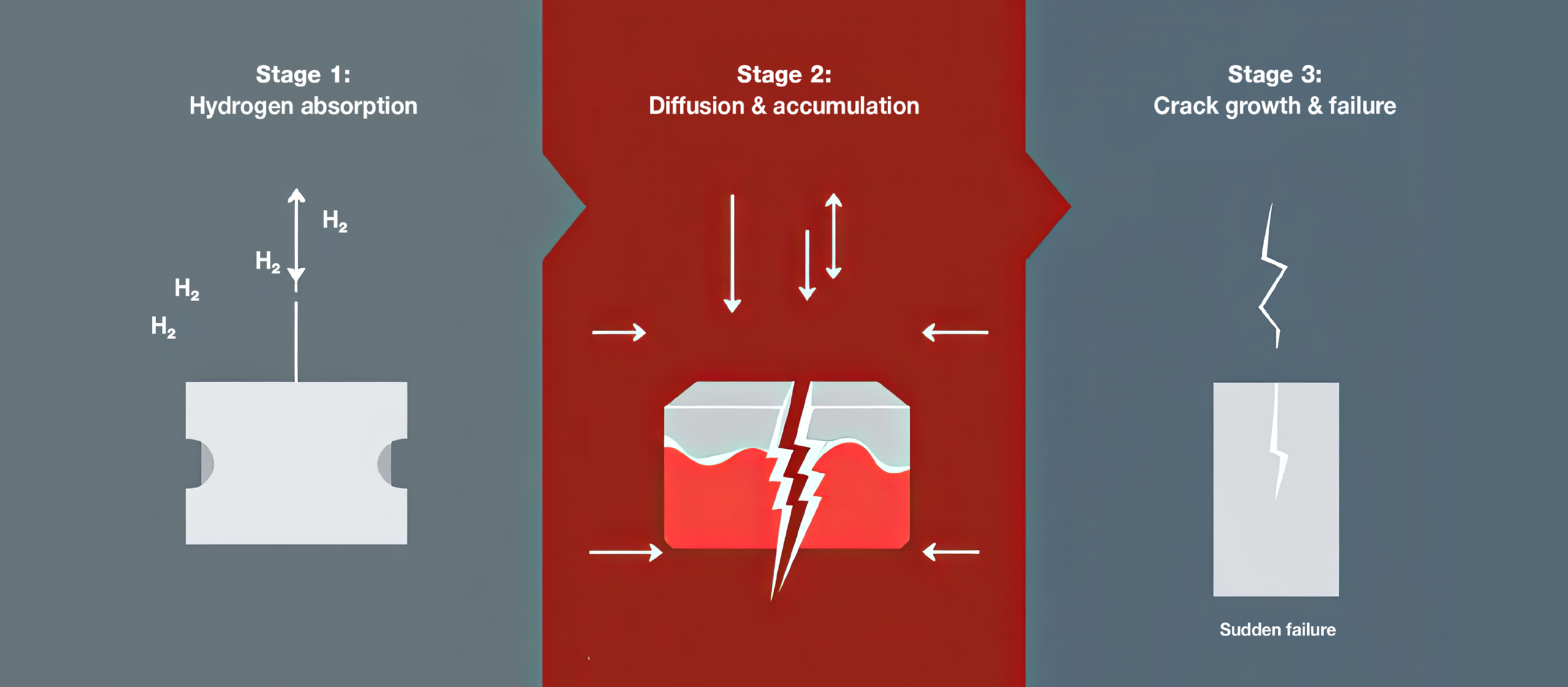
Risk 3. Compatibility with your metals and process
Not every cleaner works on every metal. Aluminium, copper alloys and mixed-metal assemblies all have specific requirements. A product that performs well on steel may cause staining or surface reactions on softer metals.
Similarly, your downstream processes matter. If parts go from the wash machine to a coating, a weld or a measurement stage, the cleanliness spec at each handover is critical. A cleaner that leaves residue, alters surface tension or interacts with a subsequent fluid is not a neutral choice.
This is a technical risk, and it is a real one. It is also exactly what compatibility testing exists to address.
Risk 4. Your team learning new procedures
A new cleaning product often means new dosing parameters, new bath maintenance routines, and new things to monitor. Operators who have been running the same process for years will need to adjust. That takes time and, done poorly, introduces errors.
This is a people risk as much as a technical one, and it is often underestimated. Training is not a nice-to-have at the end of a conversion. It is part of the conversion.
Risk 5. Supplier support not living up to the promise
Perhaps the most common source of pain in any chemical switch is this: the supplier was attentive during the sales process and largely absent afterwards. Questions go unanswered. The service visit that was promised never materialises. The process drifts, and there is no one to call.
This is not a small risk. An unstable cleaning process is a direct threat to production quality and throughput. And it is a risk that has nothing to do with the chemistry itself. It is entirely about who you are choosing to work with.
Learn more about how to address the risks
So far, so fair. Now the harder question
Every risk listed above is legitimate. None of them are invented to be dismissed. If you are considering switching your industrial parts cleaner, you should think carefully about all of them.
But here is the question that often does not get asked with the same rigour: what is the risk of not switching?
Because staying with your current cleaning process also carries risks. They are just slower, quieter, and easier to absorb until they are not.
The cost of standing still:
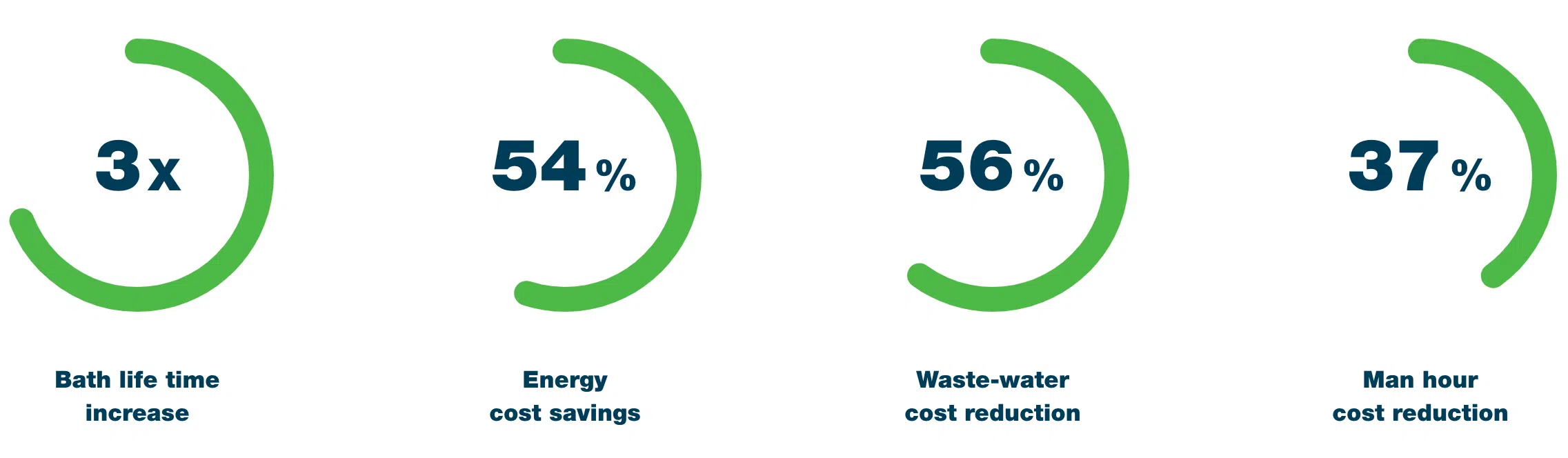
- Running your wash bath at 60-65°C when a better-formulated cleaner would perform at 45°C. That is up to 50% more energy consumption, every shift, every day.
- Changing your bath every few weeks because the cleaner degrades quickly, taking wastewater disposal costs with it.
- Accepting a cleaning result that is borderline acceptable, and hoping quality control does not notice.
- Getting no service visits, no process optimisation, no one checking whether your nozzles are blocked or your oil skimmer is working.
- Paying a low price per litre for a product whose total cost of ownership is substantially higher than the alternative.
The risks of switching are limited. They occur during a defined conversion window, and a well-managed conversion addresses each one directly.
The risks of not switching cleaner are ongoing. They accumulate in your energy bill, your wastewater costs, your reject rate and your process instability. They do not announce themselves. They just quietly add up.
That is the comparison worth making.
Learn more about the comparison
FAQ
Q. How long does a conversion typically take?
The physical conversion, draining the bath, cleaning the machine and refilling with the new product, typically takes between half a day and a full day. This varies with machine size, contamination levels and your wastewater handling setup. We schedule it around your production calendar to minimise disruption.
Q. Do we need to test before committing to a conversion?
Yes, and any reputable supplier will insist on it. A compatibility test against your specific parts, metals, contaminants and machine is the foundation of a successful conversion. Without it, you are guessing. With it, you are confirming.
Q. What happens if the new product does not perform as expected after the switch?
A good supplier does not disappear after implementation. Performance issues are addressed on site. The first 21 days after a conversion are a critical period, and a service visit during that window is standard practice, not an optional extra.
Q. We have used the same cleaner for years. Is there a real benefit to switching?
Possibly yes, possibly no. The only way to know is to run a Total Cost of Ownership analysis against your current process. Energy consumption, bath lifetime, wastewater disposal, product dosage and downtime all factor in. The answer may surprise you.
Q. How do we evaluate whether a new supplier will actually support us after the sale?
Ask for references. Ask specifically about what happens after implementation. A supplier who leads with a structured service model, named contact, regular visits, continuous process monitoring, is telling you something important about how they operate. One who leads only on product price is also telling you something.
What if the CFO takes a go at me?
Environment, social and governance
At DST-CHEMICALS, sustainability is at the heart of everything we do. We engaged with key stakeholders, including our team of suppliers, to ensure we focused on what truly mattered. Ready to see the full picture?
Have a look at our ESG report, where we share the next steps in our journey to sustainability.