The Complete guide to removing oxidation from aluminium
Realizing the benefits of
taking TCO into consideration
for industrial cleaning
Table of Contents
What is aluminium oxidation?
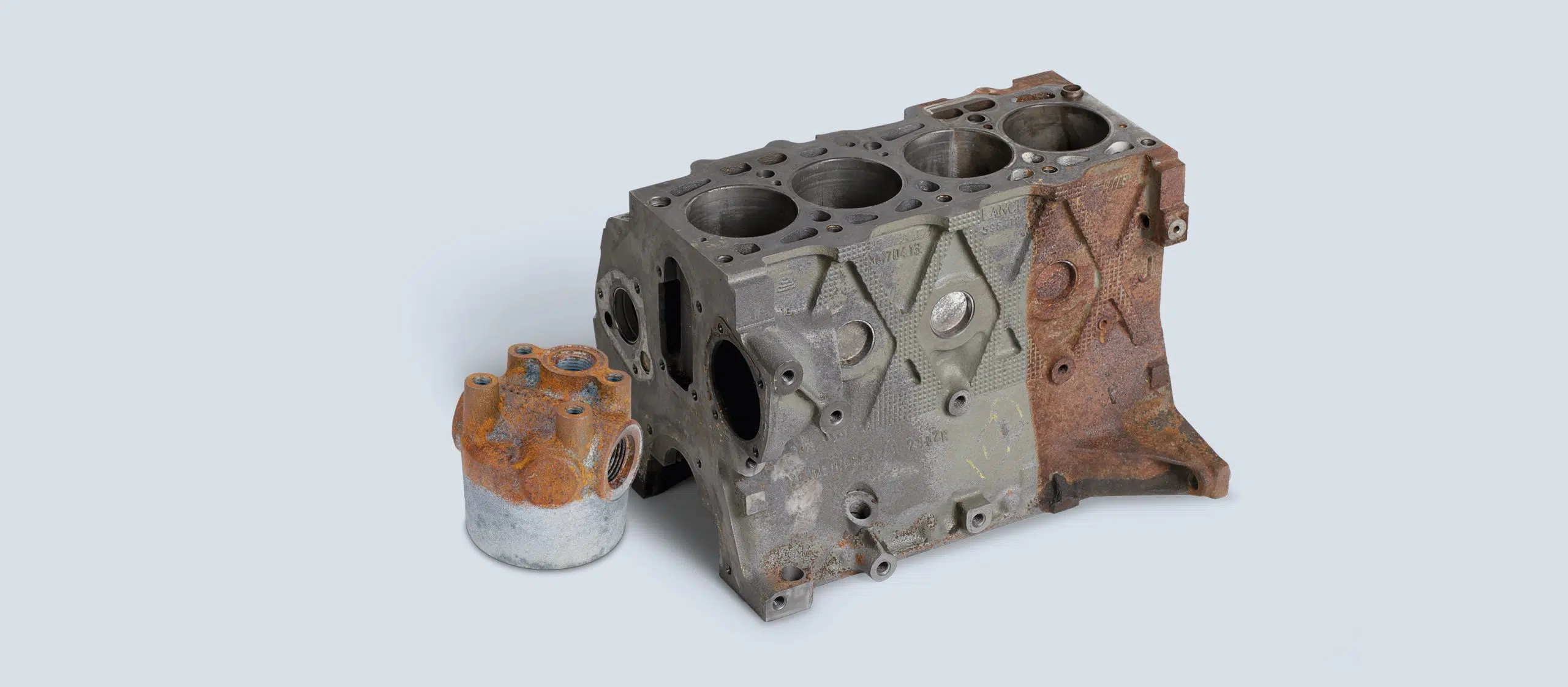
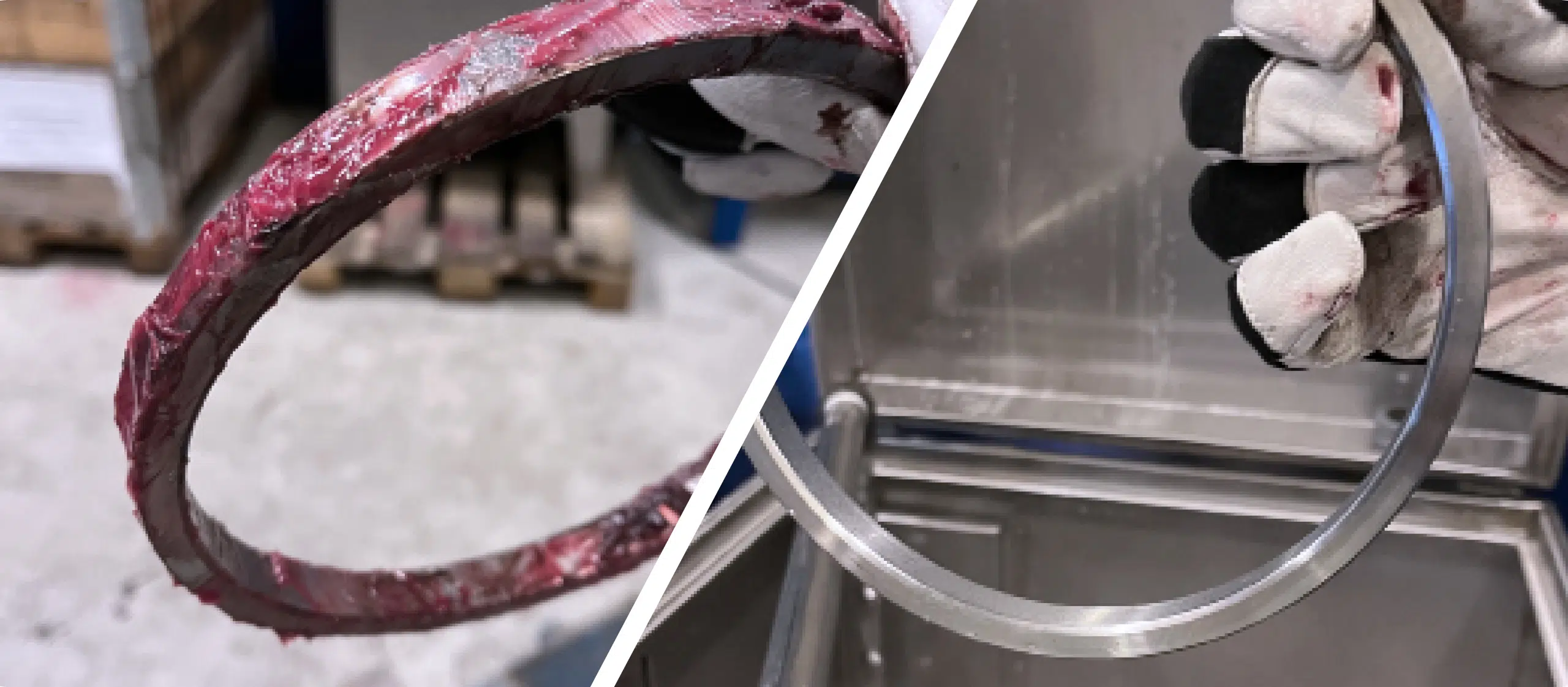
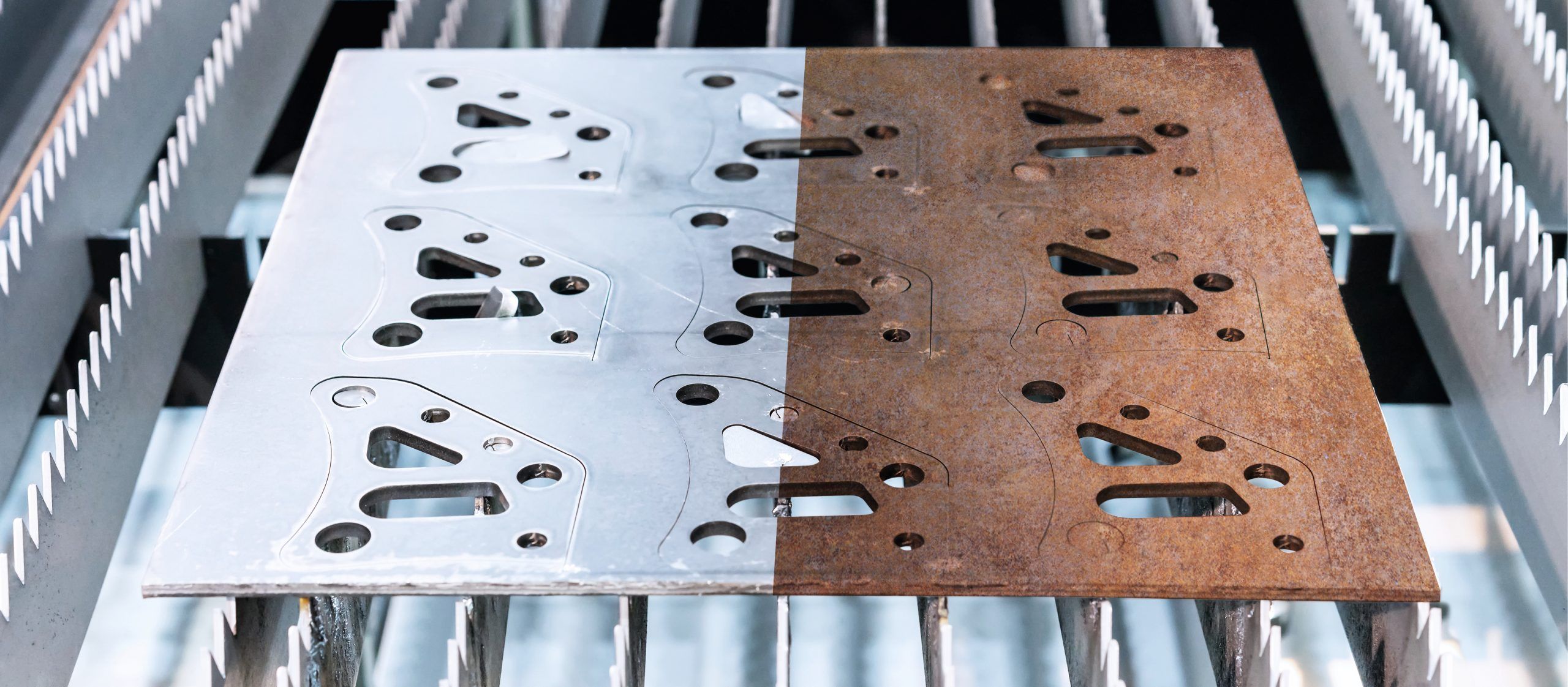
Aluminium oxidation refers to the process in which aluminium reacts with oxygen in the air, forming a thin layer of aluminium oxide on the surface of the metal. This layer is typically white or grey in colour and can give the aluminium a dull and pitted appearance. While aluminium oxide is a protective barrier that helps prevent further corrosion, excessive oxidation can lead to deterioration of the metal.
Note that aluminium oxidation is different from rust, a form of iron oxide that occurs when iron reacts with oxygen and moisture. Rust is typically reddish-brown and is commonly associated with ferrous metals like steel. Corrosion, on the other hand, is a general term that refers to the degradation of metals through chemical reactions with their environment.
Read more about corrosion and rust removal in industrial settings here
The appearance of aluminium oxidation can vary depending on the severity of the corrosion. In its initial stages, oxidation may appear as a dull, whitish film on the surface of the aluminum. As the corrosion progresses, the oxidation may develop into a more noticeable powdery or flaky texture, eventually leading to pitting or discoloration of the metal surface.
Aluminium oxidation occurs due to the natural reactivity of aluminium with oxygen in the air. When aluminium is exposed to moisture and air, a chemical reaction occurs, forming aluminium oxide on the surface of the metal. Factors such as exposure to saltwater, pollution, and harsh chemicals can accelerate the oxidation process, leading to more severe corrosion. Regular cleaning and maintenance can help prevent and remove oxidation from aluminium surfaces, preserving the metal’s appearance and structural integrity.
Step by step: 3 ways to clean oxidation from aluminium
Here are 3 methods for cleaning and removing oxidation from aluminium surfaces: Pressure washing, chemical cleaning, and steam cleaning.
Pressure washing: Pressure washing involves using high-pressure water spray to clean surfaces, including aluminium. The force of the water can dislodge dirt, grime, and oxidation from the surface, making it an effective method for cleaning large areas quickly. However, pressure washing may not be suitable for delicate or intricate aluminium surfaces, as the high pressure can potentially damage the metal or strip away protective coatings.
Chemical cleaning: Chemical cleaning involves using specialized cleaners and polishes specifically designed for aluminium surfaces. These cleaners work by breaking down oxidation and other contaminants. Chemical cleaning is a targeted approach that can be used on smaller or more delicate aluminium surfaces where pressure washing may be too harsh.
Steam cleaning: Steam cleaning uses high temperature to clean and sanitize surfaces, including aluminium. The heat and moisture help to loosen dirt and oxidation, making it easier to remove with a cloth or towel. Steam cleaning is a chemical-free method that can be as powerful as pressure washing for stubborn or deep-seated oxidation.
Each method has its own advantages and considerations, so it is essential to choose the most suitable method based on the specific requirements of the aluminium surface being cleaned. Consider factors such as the size of the area, the level of oxidation, the type of aluminium, and any protective coatings or finishes when selecting the cleaning method.
In doubt? Come, let’s find the right method for you
How to make aluminium shine
After cleaning aluminium surfaces to remove oxidation and dirt, there are several methods to restore shine to the metal.
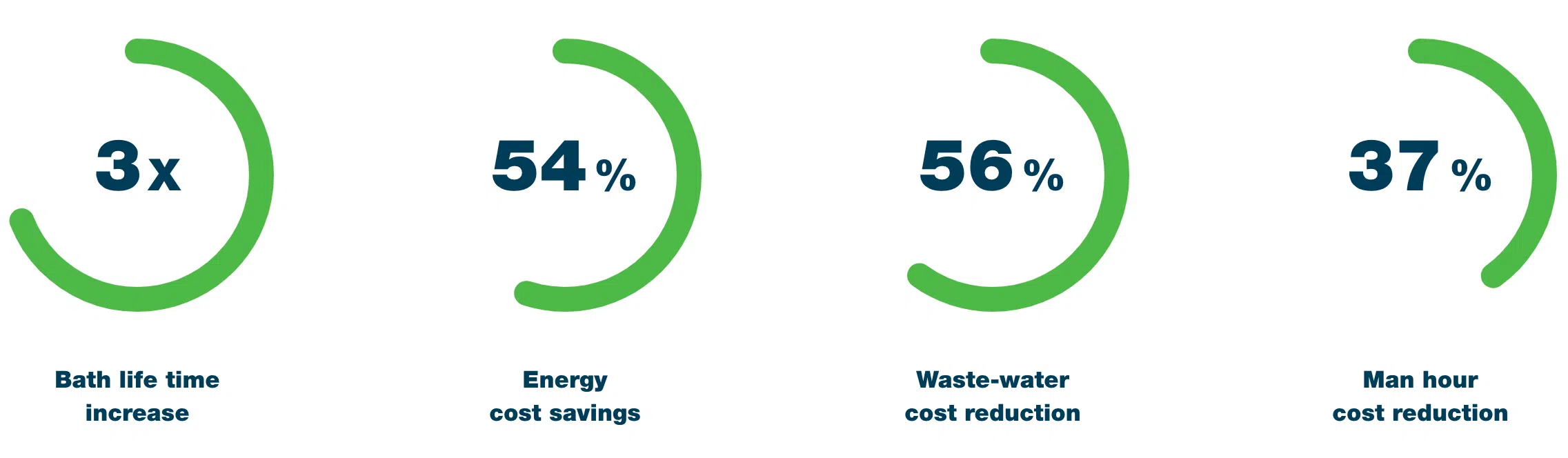
The DST-WAY: At DST-CHEMICALS, we have products to cover your exact needs. Even if you are looking for a way to reenergize your aluminium parts. We recommend using non-alkaline products. The lower the pH-value, the better. As a rule of thumb, we’d say a pH-value ranging from 2-5 depending on the part. If you are looking to prevent additional oxidation on aluminum surfaces, we suggest using our DST-Alu Rinse. This product is a 2% solution that provides temporary protection against further oxidation on aluminum. The mechanism involves penetrating the rust and corrosion, effectively breaking down the oxide layers that have accumulated on the metal.
Aluminium brightener: Aluminium brighteners are commercial products that can help to remove oxidation and restore shine to aluminium surfaces. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper application, which involve diluting the brightener with water, applying it to the surface, and rinsing it off after a specific time. Aluminium brighteners can be effective in brightening and shing aluminium surfaces.
Aluminium polish paste: Aluminium polish paste is another effective product for shining aluminium surfaces. Apply a small amount of the paste onto a damp cloth and gently rub it onto the aluminium surface in circular motions. The abrasive particles in the paste help to remove oxidation and scratches while restoring shine to the metal. Buff the surface with a clean, dry cloth to reveal a glossy.
Why remove oxidation from aluminium?
There are several reasons why it is important to remove oxidation from aluminium:
Functionality: When aluminium is oxidised, it forms a layer on its surface, which can prevent proper adhesion when welding or painting. This can lead to weak welds or paint peeling, compromising the quality and durability of the final product. Additionally, oxide layers can interfere with the assembly of aluminium parts, causing difficulties in fitting components together correctly. By removing oxidation, the surface of the aluminium is cleaned and prepared for seamless assembly, ensuring that parts fit together correctly.
Corrosion prevention: Oxidation is a form of corrosion that can deteriorate aluminium surfaces over time. If left untreated, oxidation can weaken the metal and lead to structural damage or pitting. By removing oxidation promptly, you can prevent further corrosion and extend the lifespan of aluminium surfaces.
Health and safety: Oxidised aluminium can release harmful particles into the air or onto surfaces, posing potential health risks to individuals who meet the metal. By removing oxidation, you can minimize the risk of exposure to these harmful particles and create a safer environment.
Maintenance and longevity: Regularly removing oxidation from aluminium surfaces is an essential part of maintenance to ensure the metal remains in good condition. By addressing oxidation early on, you can maintain the integrity and longevity of aluminium surfaces, reducing the need for costly repairs or replacements in the future.
Improved performance: Oxidized aluminium surfaces may not function as effectively as non-oxidized surfaces, particularly in applications where conductivity or reflectivity is important. By removing oxidation, you can restore the performance of aluminium components and ensure they function optimally.
Ease of cleaning: As mentioned, removing oxidation from aluminium is easier when done properly. Oxidation can become more challenging to remove over time, requiring more time and effort to restore the shine and lustre of the metal. By addressing oxidation early on, you can make the cleaning process more efficient and effective.