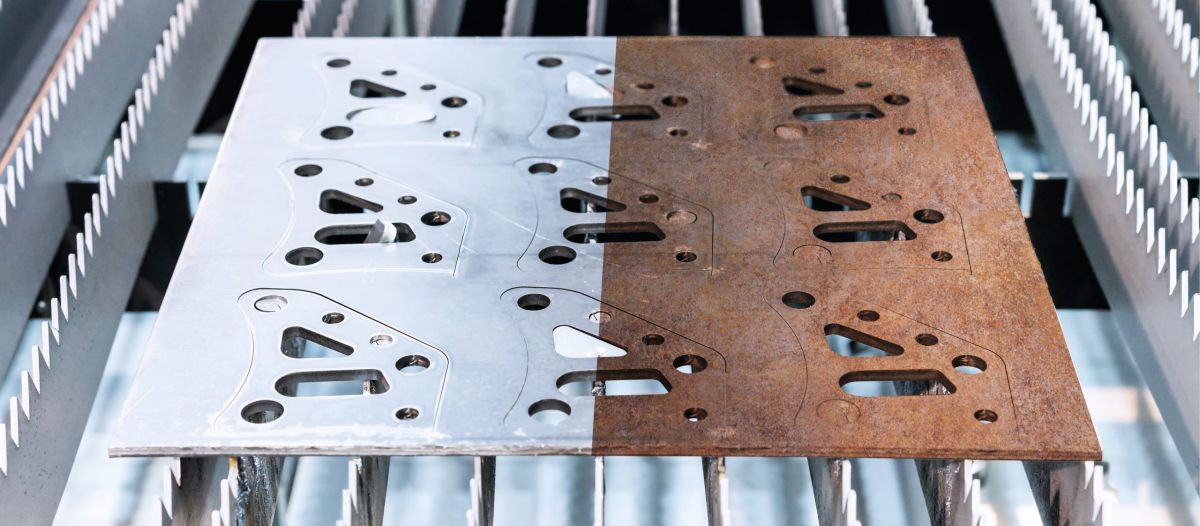
Rust is a common problem that can plague equipment and machinery, causing components to deteriorate and leading to decreased efficiency and productivity. To protect equipment and ensure operational efficiency, it is important to address rust removal and prevention effectively. In this blog post, we will explore the importance of rust removal in prolonging the lifespan of equipment and preventing costly repairs and more.
Table of Contents
What is rust and how does it form?
Rust, also known as iron oxide, is a reddish-brown coating that forms on iron and steel when exposed to oxygen and moisture. The process of rust formation, scientifically known as corrosion, occurs when iron reacts with oxygen and water, leading to the breakdown of the metal’s surface. While rust may appear harmless at first glance, it can have a detrimental effect on industrial parts if left untreated.
Rust can weaken the structural integrity of equipment, causing components to deteriorate and potentially leading to equipment failure. This can result in costly repairs, downtime, and loss of productivity for businesses. In addition, rust can also impact the efficiency and performance of equipment, reducing its lifespan and increasing maintenance costs over time.
The financial and operational risks associated with untreated rust issues are significant. Equipment that is affected by rust may experience decreased efficiency, leading to higher energy consumption and reduced output. In addition, rust can compromise the safety of equipment and pose risks to employees working with or around the affected machinery. Furthermore, untreated rust can escalate into more severe corrosion problems, resulting in the need for costly replacements or repairs.
To protect industrial equipment and maintain operational efficiency, it is crucial to address rust issues properly and effectively. Regular inspection and maintenance, along with proper rust removal techniques, can help prevent the formation of rust and prolong the lifespan of equipment. By investing in rust removal and prevention, businesses can mitigate the financial and operational risks associated with rust issues and ensure the smooth functioning of their equipment.
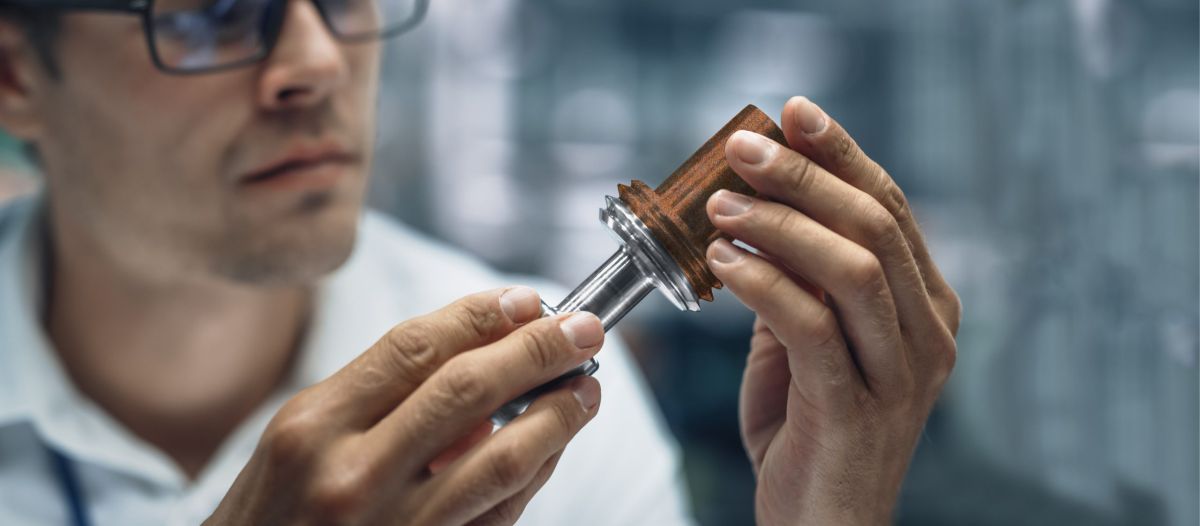

Exploring industrial rust removers
When it comes to industrial rust removal, there are several types of rust removers available on the market, each with its own unique properties and applications. Some common types of rust removers include:
Chemical rust removers: These solutions contain acidic or alkaline compounds that break down rust from metal surfaces. Examples of chemical rust removers include phosphoric acid-based products, citric acid solutions, and rust converters.
Mechanical rust removers: Mechanical rust removers, such as wire brushes, sandpaper, and abrasive pads, physically scrub away rust from metal surfaces. These tools are effective for smaller rust spots and surface-level corrosion.
Electrolytic rust removers: Electrolytic rust removal involves using an electric current and an electrolyte solution to remove rust from metal surfaces. This method is effective for larger rusted areas and can be used on delicate or complex equipment.
What to consider when selecting the rust remover
When selecting the appropriate rust remover for a specific application, there are several factors to consider:
Type and extent of rust: Consider the type and severity of rust present on the equipment. Some rust is present on the equipment. Some rust removers are more effective for light surface rust, while others are better suited for heavy corrosion.
Material compatibility: Ensure that the rust remover is compatible with the material of the equipment being treated. Some chemicals can damage certain metals or coatings.
Safety and environmental impact: Consider the safety and environmental implications of the rust remover. Choose products that are safe to use and eco-conscious.
The process of rust removal typically involves applying the rust remover to the affected area, allowing it to penetrate and break down the rust, and then scrubbing or rinsing off the rust residue. For more stubborn rust, multiple applications or a combination of different rust removal methods may be necessary.
Rust prevention strategies
In addition to using rust removers to address existing rust issues, implementing rust prevention strategies is essential for protecting industrial equipment and ensuring its longevity. One of the most effective ways to prevent rust formation is with protective coatings and sealants. These products create a barrier between the metal surface and external elements, such as oxygen and moisture, that can cause corrosion.
Some common types of protective coatings and sealants used for rust prevention include:
Paints and primers: Applying paint or primer to metal surfaces can help protect against rust formation by providing a protective barrier. Epoxy, urethane, and enamel paints are commonly used for industrial applications.
Corrosion inhibitors: Corrosion inhibitors are chemicals that can be applied to metal surfaces to prevent rust formation. These inhibitors form a protective film on the metal, preventing rust-causing elements from meeting the surface.
Galvanizing: Galvanizing involves applying a layer of zinc to metal surfaces through a hot-dip or electroplating process. This zinc coating acts as a sacrificial anode, protecting the underlying metal from corrosion.
Additionally, besides the use of protective coatings and sealants, implementing regular maintenance and inspection routines is crucial for preventing rust on industrial equipment. Regularly inspecting equipment for signs of rust, addressing any issues promptly, and conducting preventive maintenance can help identify and address potential rust risks before they escalate into more severe problems.
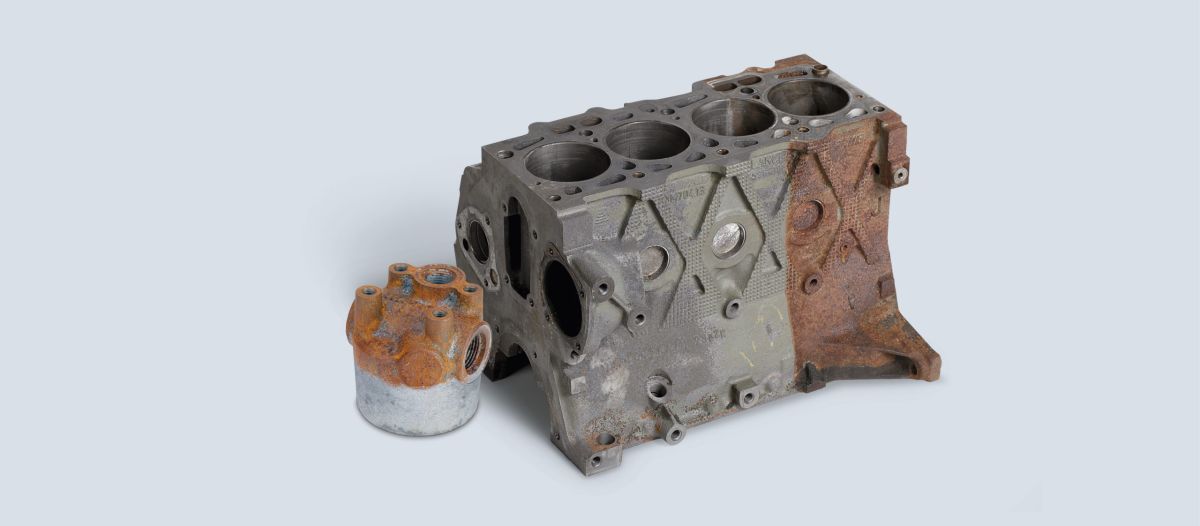

How can we help you with rust removal?
The task of rust removal can often pose significant challenges, given the ease with which rust forms and the difficulty in effectively eliminating it, not to mention the potential for soaring costs. In response to this persistent issue, we have introduced the innovative DST-DERUST solution. This product offers a straightforward yet powerful functionality, boasting three key advantages. Firstly, it significantly reduces energy expenses by operating efficiently at room temperature, thereby enhancing cost-effectiveness and yielding substantial savings on energy consumption. Secondly, the water-based DST-DERUST products maintain a neutral pH level ranging from 5.7 to 6.6, eliminating the need for labelling and ensuring a safer work environment for employees. Lastly, the DST-DERUST products require minimal handling as they effectively remove various forms of corrosion and rust, including red iron oxides. This seamless process allows for post-treatment activities such as laser welding without any hindrance, exemplifying the versatility and convenience offered by DST-DERUST.
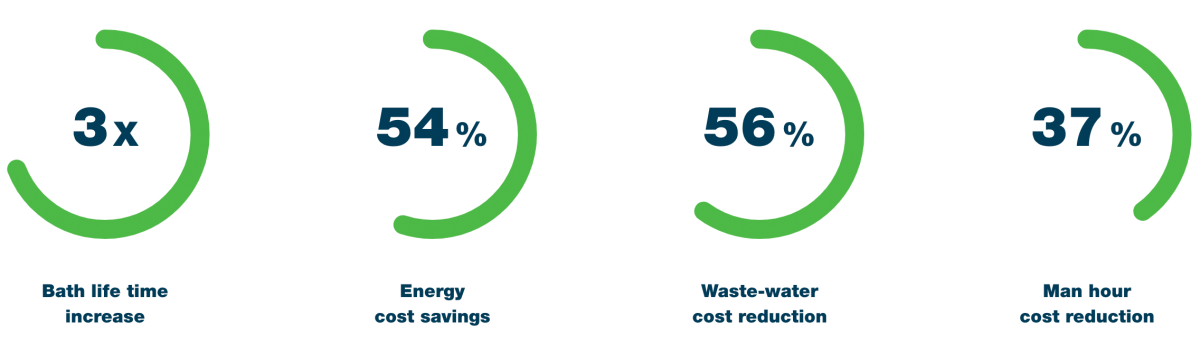
These numbers below are your potential and maybe more.
Try out this calculator and see for yourself.
Questions & Answers
What is rust?
Rust is a form of corrosion that occurs when iron or steel is exposed to oxygen and moisture, causing a chemical reaction that forms iron oxide. Rust can weaken metal structures and surfaces, leading to deterioration and potential failure over time.
What is the difference between rust, oxidation, and corrosion?
- Rust specifically refers to the reddish-brown iron oxide that forms when iron or steel reacts with oxygen and moisture.
- Oxidation is a chemical reaction that occurs when a material interacts with oxygen. While rust is a specific type of oxidation that affects iron and steel, oxidation can occur with other materials as well.
- Corrosion is a broader term that refers to the deterioration of materials, including metals, due to chemical or electrochemical reactions with their environment. Rust is a type of corrosion that affects iron and steel.
Nick Bjerregaard
International Process & Technical Manager
Technical Manager at DST-CHEMICALS: 20 years of chemical industry experience, driving innovation, efficiency, and environmental sustainability.
Environmental, social and governance
At DST-CHEMICALS, sustainability is at the heart of everything we do. We engaged with key stakeholders, including our team of suppliers, to ensure we focused on what truly mattered. Ready to see the full picture? Keep an eye out for our ESG report, where we share the next steps in our journey to sustainability.

